Objective
Our objective is to learn how to connect to a database from a Java program and then, using SQL statements to manipulate on the database. Case study with edit customer information application.
Download
– You need to install MySQL on your computer, and possibly a MySQL Workbench to easy to create a database and its tables from a GUI (see the topic SQL basic)
– You also need to download Eclipse http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/, you could download the standard version or the IDE for Java EE developers (this version will be needed in web applications)
– You have to download a MySQL driver to connect to a database from a Java program: http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/j/. And the put the .jar (in the downloaded package) into the eclipse: right click on JRE lib of the project -> choose the build path -> choose edit -> click on the “add extension jar files” and the point out to the path to the .jar file.
Connection
First of all, you have to connect to a database before using it. Assume that we have a database for a hotel management in MySQL. As studied in the DAO pattern tutorial, we need to create a connection to the DB in the constructor of DAO class:
public DAO(){
if(con == null){
String dbUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/hotel?autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false";
String dbClass = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
try {
Class.forName(dbClass);
con = DriverManager.getConnection (dbUrl, "root", "ppp");
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Note that you must modify three parameter to adapt your config:
dbClass = “com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”; –do not change if you use MySQL too.
String dbUrl = “jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/hotel“; — change the port and the name of your DB.
getConnection (dbUrl, “root”, “ppp“); — change “ppp” to your password to connect to your MsSQL
Assume that, in the hotel DB, we have a table naming tblclient which has following columns: id, name, idcard, address, email, tel, note. And at the model level of code, we also have a model class Customer with respective attributes: id, name, idcard, address, email, tel, note.
Using Statement
- Advantage: The sql string is intuitive and easy to read and understand.
- Inconvenient: We have to pay attention in the type of data to add open-close pair of “\'” for the data of type String, Date. This always leads programmer to make some mistake in sql syntax. Therefore, this is NOT recommended for professional coding usage.
/**
* add a new @client into the DB
* using Statement - NOT recommended for professional coding
* @param client
*/
public void addCustomer(Customer client){
String sql = "INSERT INTO tblclient(name, idcard, address, tel, email, note) "
+ "VALUES('" + client.getName() + "'," //name
+ "'" + client.getIdCard() + "'," //idcard
+ "'" + client.getAddress() + "'," //address
+ "'" + client.getTel() + "'," //tel
+ "'" + client.getEmail() + "',"; //email
if(client.getNote() == null) sql+= "NULL)"; //note
else sql+= "'" + client.getNote() + ")";
try{
Statement ps = con.createStatement();
ps.executeUpdate(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
//get id of the new inserted client
ResultSet generatedKeys = ps.getGeneratedKeys();
if (generatedKeys.next()) {
client.setId(generatedKeys.getInt(1));
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Using PreparedStatement
This replaces the input parameters in the sql string by a “?” and then, set value for each of them. This is acceptable for professional coding.
/**
* add a new @client into the DB
* using PreparedStatement - acceptable for professional coding
* @param client
*/
public void addCustomer(Customer client){
String sql = "INSERT INTO tblclient(name, idcard, address, tel, email, note) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?)";
try{
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
ps.setString(1, client.getName());
ps.setString(2, client.getIdCard());
ps.setString(3, client.getAddress());
ps.setString(4, client.getTel());
ps.setString(5, client.getEmail());
ps.setString(6, client.getNote());
ps.executeUpdate();
//get id of the new inserted client
ResultSet generatedKeys = ps.getGeneratedKeys();
if (generatedKeys.next()) {
client.setId(generatedKeys.getInt(1));
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Using procedure in DB + CallableStatement in Java
At this level, all sql statements are pre-coded in DB in the form of stored procedure. Thus, the stored procedure is independent from the programming language. At the Java level, we just call them to execute. This is highly recommended for professional coding.
/**
* add a new @client into the DB
* using Store procedure - highly recommended for professional coding
* @param client
*/
public void addCustomer(Customer client){
String sql = "{call client_add(?,?,?,?,?,?,?)}";
try{
CallableStatement ps = con.prepareCall(sql);
ps.setString(1, client.getName());
ps.setString(2, client.getIdCard());
ps.setString(3, client.getAddress());
ps.setString(4, client.getTel());
ps.setString(5, client.getEmail());
ps.setString(6, client.getNote());
ps.registerOutParameter(7, Types.INTEGER);
ps.execute();
//get id of the new inserted client
client.setId(ps.getInt(7));
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Note that we have to define a procedure in the DB. In MySQL: right click on stored procedure -> create stored procedure and type the following code:
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `client_add`(IN clientname VARCHAR(255),
IN idcard varchar(255), IN address varchar(500), IN tel varchar(255),
IN email varchar(255), IN note varchar(500), OUT clientid INT(10))
BEGIN
INSERT INTO tblclient(name, idcard, address, tel, email, note)
VALUES(clientname,idcard,address,tel,email,note);
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() INTO clientid;
END
Complete example: edit customer information
Description of the module
This is a module of customer management. In which, the manager searches the customer by name and then, chooses the customer from the result list to edit. After modifying some attribute, the manager clicks update to update the customer information.
Database
Assume that, in the hotel DB, we have a table naming tblclient which has following columns: id, name, idcard, address, email, tel, note.
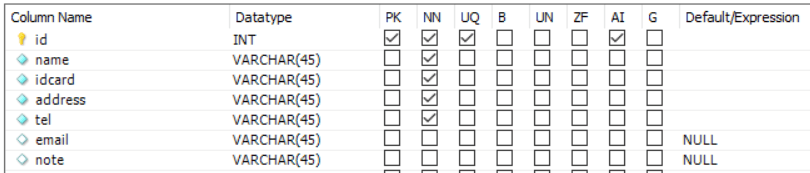
Design
Based on the MVC model, the module is designed at three levels (there are some relationships between view classes and entity class are omitted to easy follow the diagrams):
- At the model level, there is only an entity class of Customer
- At the control level, there are two classes: DAO is a general DAO class and, CustomerDAO to provide two methods to manipulate on the tblclient table: searchCustomer() to search all customers whose name contains the entered keyword. editCustomer() to update the information of the input customer.
- At the view level, there are two classes: SearchCustomerFrm is the form to search and choose the customer to edit. EditCustomerFrm is the form to edit information of the chosen customer.

The scenario to work of this module is follow (each step in the scenario corresponds to a step in the sequence diagram):
- The manager enters the keyword and clicks on the search button on the SearchCustomerFrm
- The actionperformed() method is called
- The actionperformed() method calls the searchCustomer() method of the class CustomerDAO
- The searchCustomer() executes
- The searchCustomer() method calls the Customer class to build the founded entities
- The Customer class packs the entity objects
- The customer class returns the packed objects to the search method
- The search method returns the results to the actionperformed()
- The actionperformed() method displays the results to the manager
- The manager choose the customer to modify information
- The method mouseClicked() is called
- This method call the EditCustomerFrm
- The constructor of EditCustomerFrm() is called
- The form is displayed to the manager with the current information of the chosen customer
- The manager modifies some attributes and clicks on update button
- The actionperformed() method of the class is called
- This method calls some setter methods of Customer class to set new value for the customer object
- The setter methods execute
- The Customer class returns the updated object to the actionperformed() method
- This method calls the edit method of the CustomerDAO class
- The editCustomer() method executes
- The edit method return to the actionperformed() method
- This method show the success message and closes the forms.

Code (bottom up)
Class: Customer
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Customer implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 20210811004L;
private int id;
private String name;
private String idCard;
private String address;
private String tel;
private String email;
private String note;
public Customer() {
super();
}
public Customer(String name, String idCard, String address, String tel, String email, String note) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.idCard = idCard;
this.address = address;
this.tel = tel;
this.email = email;
this.note = note;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getIdCard() {
return idCard;
}
public void setIdCard(String idCard) {
this.idCard = idCard;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getNote() {
return note;
}
public void setNote(String note) {
this.note = note;
}
}
Class: DAO
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
public class DAO {
public static Connection con;
public DAO(){
if(con == null){
String dbUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/hotel?autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false";
String dbClass = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
try {
Class.forName(dbClass);
con = DriverManager.getConnection (dbUrl, "root", "xxx");
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Class: CustomerDAO
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.Types;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import model.Customer;
public class CustomerDAO extends DAO{
/**
* search all clients in the tblClient whose name contains the @key
* using PreparedStatement - recommended for professional coding
* @param key
* @return list of client whose name contains the @key
*/
public ArrayList<Customer> searchCustomer(String key){
ArrayList<Customer> result = new ArrayList<Customer>();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM tblclient WHERE name LIKE ?";
try{
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, "%" + key + "%");
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
Customer client = new Customer();
client.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
client.setName(rs.getString("name"));
client.setIdCard(rs.getString("idcard"));
client.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
client.setTel(rs.getString("tel"));
client.setEmail(rs.getString("email"));
client.setNote(rs.getString("note"));
result.add(client);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* update the @client
* @param client
*/
public boolean editCustomer(Customer client){
String sql = "UPDATE tblclient SET name=?, idcard =?, address=?, tel=?, email=?, note=? WHERE id=?";
try{
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, client.getName());
ps.setString(2, client.getIdCard());
ps.setString(3, client.getAddress());
ps.setString(4, client.getTel());
ps.setString(5, client.getEmail());
ps.setString(6, client.getNote());
ps.setInt(7, client.getId());
ps.executeUpdate();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
Class: SearchCustomerFrm
import java.awt.Component;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.swing.Box;
import javax.swing.BoxLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTable;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.table.DefaultTableModel;
import jdbc.dao.CustomerDAO;
import model.Customer;
public class SearchCustomerFrm extends JFrame implements ActionListener{
private ArrayList<Customer> listCustomer;
private JTextField txtKey;
private JButton btnSearch;
private JTable tblResult;
public SearchCustomerFrm(){
super("Search customer to edit");
listCustomer = new ArrayList<Customer>();
JPanel pnMain = new JPanel();
pnMain.setSize(this.getSize().width-5, this.getSize().height-20);
pnMain.setLayout(new BoxLayout(pnMain,BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
pnMain.add(Box.createRigidArea(new Dimension(0,10)));
JLabel lblHome = new JLabel("Search a customer to edit");
lblHome.setAlignmentX(Component.CENTER_ALIGNMENT);
lblHome.setFont (lblHome.getFont ().deriveFont (20.0f));
pnMain.add(lblHome);
pnMain.add(Box.createRigidArea(new Dimension(0,20)));
JPanel pn1 = new JPanel();
pn1.setLayout(new BoxLayout(pn1,BoxLayout.X_AXIS));
pn1.setSize(this.getSize().width-5, 20);
pn1.add(new JLabel("Client name: "));
txtKey = new JTextField();
pn1.add(txtKey);
btnSearch = new JButton("Search");
btnSearch.addActionListener(this);
pn1.add(btnSearch);
pnMain.add(pn1);
pnMain.add(Box.createRigidArea(new Dimension(0,10)));
JPanel pn2 = new JPanel();
pn2.setLayout(new BoxLayout(pn2,BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
tblResult = new JTable();
JScrollPane scrollPane= new JScrollPane(tblResult);
tblResult.setFillsViewportHeight(false);
scrollPane.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(scrollPane.getPreferredSize().width, 250));
tblResult.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
int column = tblResult.getColumnModel().getColumnIndexAtX(e.getX()); // get the coloum of the button
int row = e.getY() / tblResult.getRowHeight(); // get the row of the button
// *Checking the row or column is valid or not
if (row < tblResult.getRowCount() && row >= 0 && column < tblResult.getColumnCount() && column >= 0) {
(new EditCustomerFrm(listCustomer.get(row))).setVisible(true);
dispose();
}
}
});
pn2.add(scrollPane);
pnMain.add(pn2);
this.add(pnMain);
this.setSize(600,300);
this.setLocation(200,10);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
JButton btnClicked = (JButton)e.getSource();
if(btnClicked.equals(btnSearch)){
if((txtKey.getText() == null)||(txtKey.getText().length() == 0))
return;
listCustomer = (new CustomerDAO()).searchCustomer(txtKey.getText().trim());
String[] columnNames = {"Id", "Name", "idCard", "Address", "Email", "Tel", "Note"};
String[][] value = new String[listCustomer.size()][columnNames.length];
for(int i=0; i<listCustomer.size(); i++){
value[i][0] = listCustomer.get(i).getId() +"";
value[i][1] = listCustomer.get(i).getName();
value[i][2] = listCustomer.get(i).getIdCard();
value[i][3] = listCustomer.get(i).getAddress();
value[i][4] = listCustomer.get(i).getEmail();
value[i][5] = listCustomer.get(i).getTel();
value[i][6] = listCustomer.get(i).getNote();
}
DefaultTableModel tableModel = new DefaultTableModel(value, columnNames) {
@Override
public boolean isCellEditable(int row, int column) {
//unable to edit cells
return false;
}
};
tblResult.setModel(tableModel);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SearchCustomerFrm view = new SearchCustomerFrm();
view.setVisible(true);
}
}
Class: EditCustomerFrm
import java.awt.Component;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.Box;
import javax.swing.BoxLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import jdbc.dao.CustomerDAO;
import model.Customer;
public class EditCustomerFrm extends JFrame implements ActionListener{
private Customer customer;
private JTextField txtId, txtName, txtIdcard, txtAddress, txtEmail, txtTel, txtNote;
private JButton btnUpdate, btnReset;
public EditCustomerFrm(Customer client){
super("Edit a customer");
this.customer = client;
JPanel pnMain = new JPanel();
pnMain.setSize(this.getSize().width-5, this.getSize().height-20);
pnMain.setLayout(new BoxLayout(pnMain,BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
pnMain.add(Box.createRigidArea(new Dimension(0,10)));
JLabel lblHome = new JLabel("Edit a customer information");
lblHome.setAlignmentX(Component.CENTER_ALIGNMENT);
lblHome.setFont (lblHome.getFont ().deriveFont (20.0f));
pnMain.add(lblHome);
pnMain.add(Box.createRigidArea(new Dimension(0,20)));
txtId = new JTextField(15);
txtId.setEditable(false);
txtName = new JTextField(15);
txtIdcard = new JTextField(15);
txtAddress = new JTextField(15);
txtEmail = new JTextField(15);
txtTel = new JTextField(15);
txtNote = new JTextField(15);
btnUpdate = new JButton("Update");
btnReset = new JButton("Reset");
JPanel content = new JPanel();
content.setLayout(new GridLayout(8,2));
content.add(new JLabel("Customer ID:")); content.add(txtId);
content.add(new JLabel("Name:")); content.add(txtName);
content.add(new JLabel("Idcard:")); content.add(txtIdcard);
content.add(new JLabel("Address:")); content.add(txtAddress);
content.add(new JLabel("Email:")); content.add(txtEmail);
content.add(new JLabel("Tel:")); content.add(txtTel);
content.add(new JLabel("Note:")); content.add(txtNote);
content.add(btnUpdate); content.add(btnReset);
pnMain.add(content);
btnUpdate.addActionListener(this);
btnReset.addActionListener(this);
initForm();
this.setContentPane(pnMain);
this.setSize(600,300);
this.setLocation(200,10);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
}
private void initForm(){
if(customer != null){
txtId.setText(customer.getId()+"");
txtName.setText(customer.getName());
txtIdcard.setText(customer.getIdCard());
txtAddress.setText(customer.getAddress());
txtEmail.setText(customer.getEmail());
txtTel.setText(customer.getTel());
txtNote.setText(customer.getNote());
}
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
JButton btnClicked = (JButton)e.getSource();
if(btnClicked.equals(btnReset)){
initForm();
return;
}
if(btnClicked.equals(btnUpdate)){
customer.setName(txtName.getText());
customer.setIdCard(txtIdcard.getText());
customer.setAddress(txtAddress.getText());
customer.setEmail(txtEmail.getText());
customer.setTel(txtTel.getText());
customer.setNote(txtNote.getText());
boolean ok = (new CustomerDAO()).editCustomer(customer);
if(ok) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "Update succesfully!");
this.dispose();
}
else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "Error when updating!");
}
}
}
}